Plantain Vs Banana – two fruits that often cause confusion. While they look similar, key differences set them apart in taste, texture, and culinary uses. This article delves into the distinct characteristics of plantains and bananas, exploring their nutritional profiles, culinary versatility, and cultural significance.
What’s the Difference Between a Plantain and a Banana?
Plantains and bananas belong to the same family, Musaceae, but differ in their starch and sugar content. Bananas are typically eaten raw when ripe, featuring a sweet flavor and soft texture. Plantains, however, are starchier and less sweet, requiring cooking before consumption. They offer a savory, almost potato-like flavor when cooked.
Nutritional Showdown: Plantain vs Banana
Both plantains and bananas are nutritious powerhouses, providing essential vitamins and minerals. Bananas are a good source of potassium, vitamin B6, and vitamin C. Plantains, especially when green, boast higher levels of resistant starch, a type of fiber that promotes gut health. Ripe plantains offer a boost of vitamin A, contributing to healthy vision and skin.
- Potassium: Both are excellent sources, crucial for maintaining fluid balance and muscle function.
- Vitamin B6: Supports brain development and immune function.
- Vitamin C: A potent antioxidant, essential for tissue repair and immunity.
- Resistant Starch (Plantains): Promotes gut health and aids in blood sugar control.
- Vitamin A (Ripe Plantains): Contributes to healthy vision, skin, and immune function.
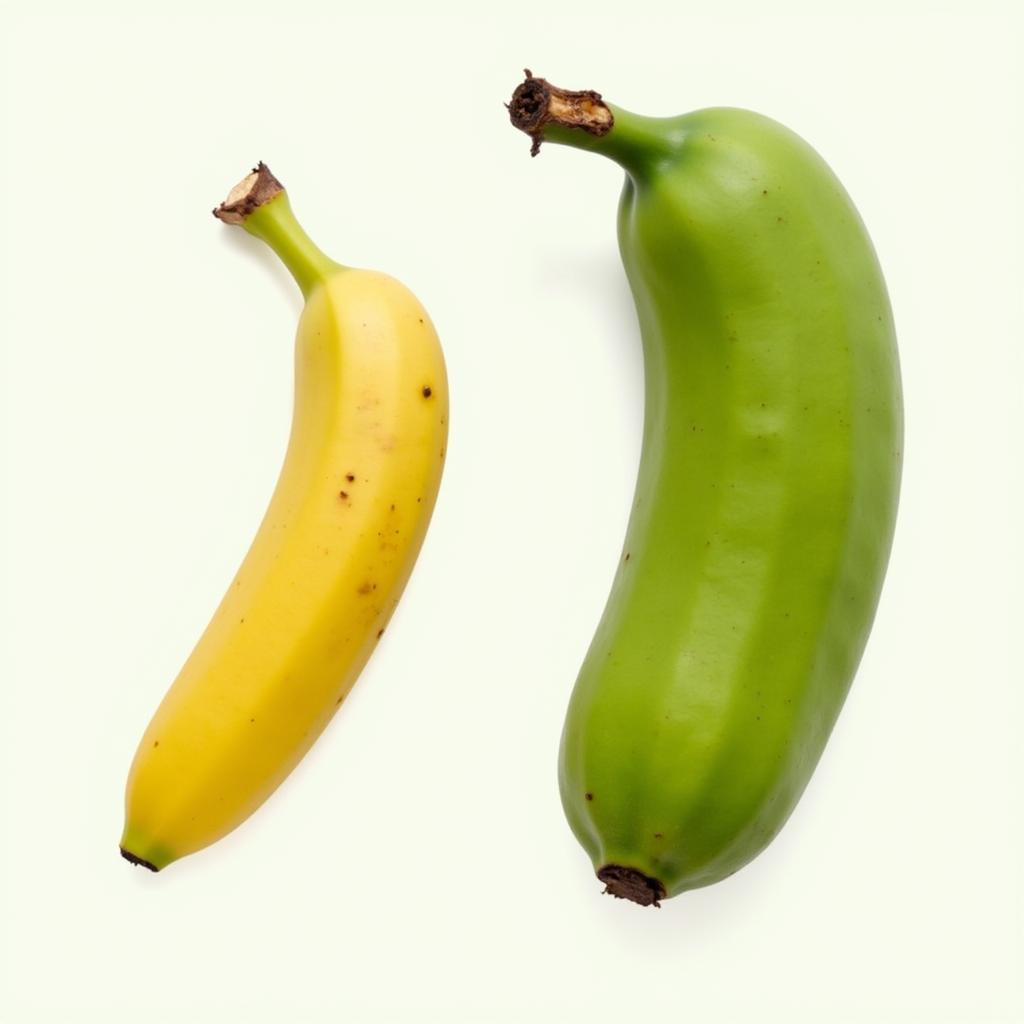 So sánh Chuối Tây và Chuối Sứ: Sự khác biệt về hình dáng, màu sắc và kích thước
So sánh Chuối Tây và Chuối Sứ: Sự khác biệt về hình dáng, màu sắc và kích thước
Culinary Adventures: From Sweet to Savory
The culinary applications of plantains and bananas diverge significantly. Bananas are enjoyed fresh in smoothies, yogurt, or as a standalone snack. Plantains, on the other hand, shine in cooked dishes. Green plantains are often fried or boiled, while riper plantains can be baked, grilled, or used in desserts.
- Green Plantains: Ideal for savory dishes like tostones (twice-fried plantain slices), mofongo (mashed plantains), and fufu (boiled and mashed plantains).
- Ripe Plantains: Perfect for sweet treats like maduros (caramelized fried plantains) or incorporated into cakes and other desserts.
“In many Latin American countries, plantains are a staple food, much like potatoes are in other parts of the world,” says Maria Sanchez, a renowned chef specializing in Latin American cuisine. “Their versatility allows them to be incorporated into countless dishes, from appetizers to desserts.”
Plantain vs Banana: A Global Perspective
Both plantains and bananas hold cultural significance in various regions. Bananas are a popular fruit globally, enjoyed as a quick and convenient snack. Plantains, however, are deeply ingrained in the cuisines of Latin America, the Caribbean, and parts of Africa, featuring prominently in traditional dishes and cultural celebrations.
 Các món ăn từ Chuối Sứ và Chuối Tây: Hình ảnh các món ăn được chế biến từ chuối sứ và chuối tây như chuối chiên, bánh chuối, sinh tố chuối…
Các món ăn từ Chuối Sứ và Chuối Tây: Hình ảnh các món ăn được chế biến từ chuối sứ và chuối tây như chuối chiên, bánh chuối, sinh tố chuối…
Spotting the Difference: A Quick Guide
While they may look similar at first glance, several key features distinguish plantains from bananas. Plantains are generally larger and thicker than bananas, with a more angular shape. Their skin can range from green to yellow to black, depending on ripeness, while bananas typically turn yellow when ripe.
- Size: Plantains are larger and thicker than bananas.
- Shape: Plantains have a more angular shape compared to the curved shape of bananas.
- Skin Color: Plantains range from green to yellow to black, while bananas typically turn yellow when ripe.
“The easiest way to tell them apart is by their size and shape,” explains Carlos Rodriguez, a botanist specializing in tropical fruits. “Plantains are noticeably larger and more robust than bananas.”
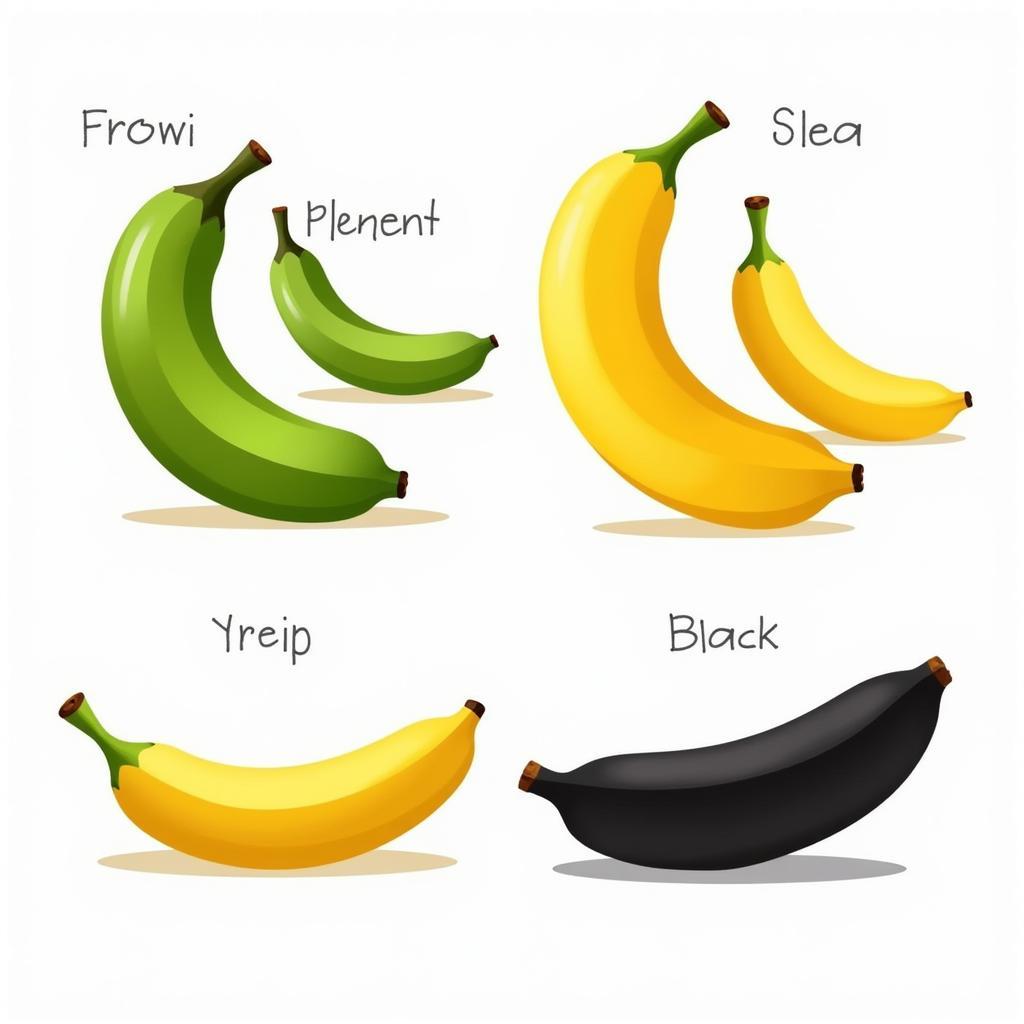 Các giai đoạn chín của chuối sứ: Hình ảnh chuối sứ ở các giai đoạn chín khác nhau, từ xanh đến vàng rồi đen, kèm theo mô tả về hương vị và độ ngọt của từng giai đoạn.
Các giai đoạn chín của chuối sứ: Hình ảnh chuối sứ ở các giai đoạn chín khác nhau, từ xanh đến vàng rồi đen, kèm theo mô tả về hương vị và độ ngọt của từng giai đoạn.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fruit
Understanding the plantain vs banana debate unlocks a world of culinary possibilities. While both offer nutritional benefits, their distinct flavors and textures make them suitable for different applications. So, whether you’re craving a sweet snack or a savory side dish, knowing the difference between these two tropical fruits ensures you choose the perfect one for your culinary needs.
FAQ
- Can you eat plantains raw?
- Are plantains healthier than bananas?
- What are some popular plantain recipes?
- How do you ripen plantains?
- Where can I buy plantains?
- Can you substitute plantains for bananas in recipes?
- What is the difference between green, yellow, and black plantains?
Common Scenarios
- Scenario 1: You’re looking for a quick and easy snack. (Choose a banana)
- Scenario 2: You’re making a savory dish like tostones. (Choose a green plantain)
- Scenario 3: You want to add a sweet element to a dessert. (Choose a ripe plantain or banana)
Related Articles
- The Ultimate Guide to Bananas
- Exploring the World of Tropical Fruits
- Healthy Eating Habits for a Balanced Diet
Khi cần hỗ trợ hãy liên hệ Số Điện Thoại: 02838172459, Email: truyenthongbongda@gmail.com Hoặc đến địa chỉ: 596 Đ. Hậu Giang, P.12, Quận 6, Hồ Chí Minh 70000, Việt Nam. Chúng tôi có đội ngũ chăm sóc khách hàng 24/7.