Classical conditioning and operant conditioning are two fundamental learning processes in behavioral psychology. They explain how we acquire new behaviors and how those behaviors are modified over time. While both involve learning through association, they differ significantly in their underlying mechanisms.
What is Classical Conditioning?
Classical conditioning, also known as Pavlovian conditioning, involves learning through association between two stimuli. A neutral stimulus becomes associated with a naturally occurring stimulus (unconditioned stimulus) that evokes an automatic response (unconditioned response). Through repeated pairings, the neutral stimulus eventually elicits the same response, now called the conditioned response, even in the absence of the unconditioned stimulus.
Pavlov’s Dog Experiment: A Classic Example
The most famous example of classical conditioning is Pavlov’s experiment with dogs. Pavlov observed that dogs naturally salivate (unconditioned response) when presented with food (unconditioned stimulus). He then paired a ringing bell (neutral stimulus) with the presentation of food. Over time, the dogs began to salivate (conditioned response) at the sound of the bell alone, even without the presence of food.
What is Operant Conditioning?
Operant conditioning, also known as instrumental conditioning, involves learning through the consequences of behavior. Behaviors followed by desirable consequences are strengthened and become more likely to occur, while behaviors followed by undesirable consequences are weakened and become less likely to occur.
Reinforcement and Punishment: Key Concepts
Operant conditioning relies on reinforcement and punishment to shape behavior. Reinforcement increases the likelihood of a behavior, while punishment decreases the likelihood of a behavior. Reinforcement can be positive (adding something desirable) or negative (removing something undesirable). Similarly, punishment can be positive (adding something undesirable) or negative (removing something desirable).
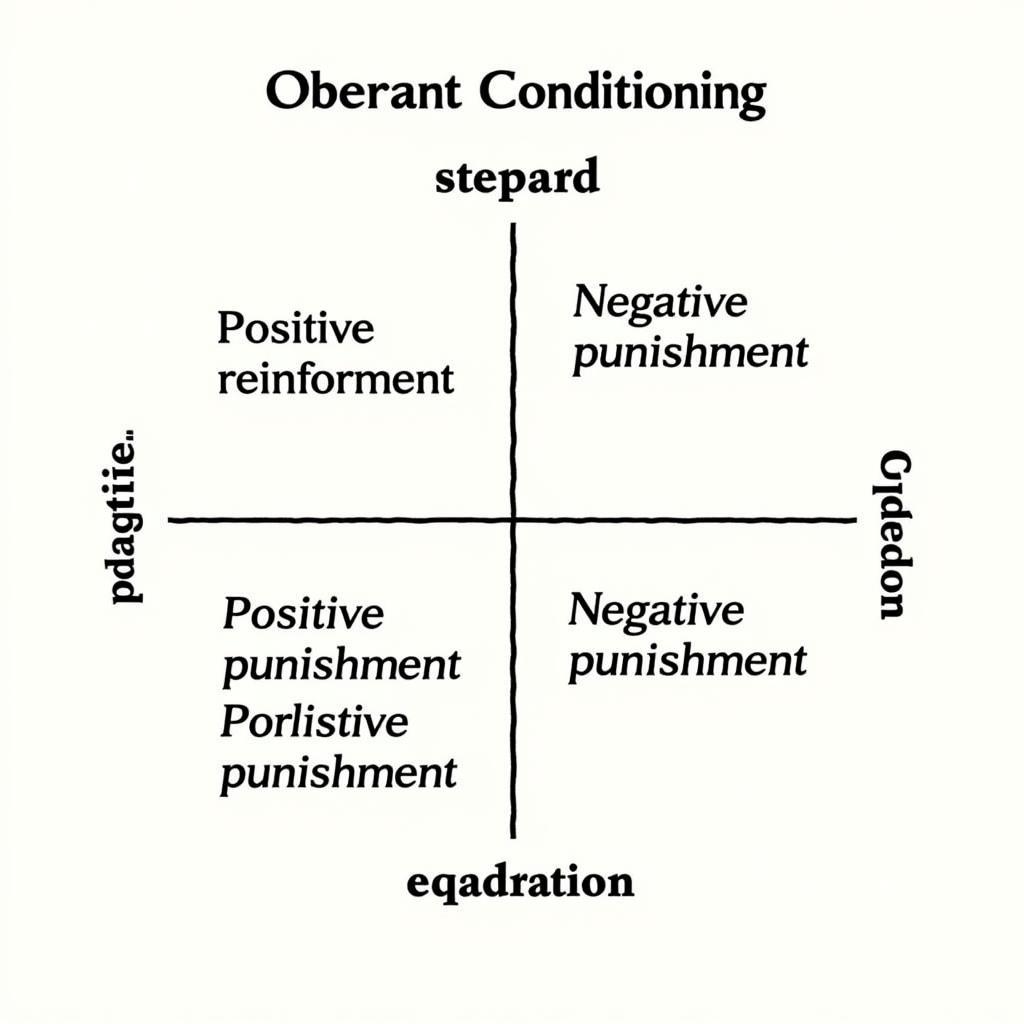 Operant Conditioning Chart: Positive and Negative Reinforcement and Punishment
Operant Conditioning Chart: Positive and Negative Reinforcement and Punishment
Classical Conditioning vs Operant Conditioning: Key Differences
The core difference between classical and operant conditioning lies in the role of the learner. In classical conditioning, the learner is passive and responds to stimuli. In operant conditioning, the learner is active and operates on the environment to produce consequences. Another key difference is the type of behavior being learned. Classical conditioning involves involuntary, reflexive responses, while operant conditioning involves voluntary, learned behaviors.
Comparing the Two Learning Processes
| Feature | Classical Conditioning | Operant Conditioning |
|---|---|---|
| Nature of Response | Involuntary, reflexive | Voluntary, operant |
| Role of Learner | Passive, responds to stimuli | Active, operates on environment |
| Basis of Learning | Association between stimuli | Consequences of behavior |
| Key Concepts | Unconditioned stimulus, conditioned stimulus, conditioned response | Reinforcement, punishment |
Conclusion: Applying Classical and Operant Conditioning
Understanding the differences between classical conditioning and operant conditioning is crucial for understanding how we learn and how we can modify our behavior. These principles are widely applied in various fields, including education, therapy, and animal training. By understanding these learning processes, we can gain valuable insights into human and animal behavior and develop effective strategies for behavior modification. Both classical conditioning and operant conditioning play significant roles in shaping our actions and reactions.
FAQ
- What is an example of classical conditioning in everyday life?
- What is an example of operant conditioning in everyday life?
- Can classical and operant conditioning occur simultaneously?
- How is classical conditioning used in advertising?
- How is operant conditioning used in parenting?
- What are the limitations of classical conditioning?
- What are the limitations of operant conditioning?
Mô tả các tình huống thường gặp câu hỏi
Người dùng thường muốn hiểu rõ hơn về sự khác biệt giữa điều kiện hóa cổ điển và điều kiện hóa thao tác, cũng như cách áp dụng chúng trong cuộc sống hàng ngày.
Gợi ý các câu hỏi khác, bài viết khác có trong web.
Bạn có thể tìm hiểu thêm về tâm lý học hành vi và các lý thuyết học tập khác trên trang web của chúng tôi.