Antigens Vs Pathogens – these two terms are often used in discussions about the immune system, but what exactly do they mean and how are they different? This article will delve into the key distinctions between antigens and pathogens, providing a comprehensive understanding of their roles in immunity and disease.
Decoding Antigens and Pathogens
What is a Pathogen?
Pathogens are disease-causing microorganisms. These microscopic invaders, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, can wreak havoc on our health. They work by entering our bodies, multiplying, and disrupting normal bodily functions, leading to illness. Think of pathogens as the “bad guys” that trigger our immune system’s defenses.
What is an Antigen?
Antigens, on the other hand, are any substance that triggers an immune response. They can be found on the surface of pathogens, but they aren’t necessarily pathogens themselves. Antigens act like “identification tags” for our immune system, signaling the presence of something foreign that needs to be neutralized.
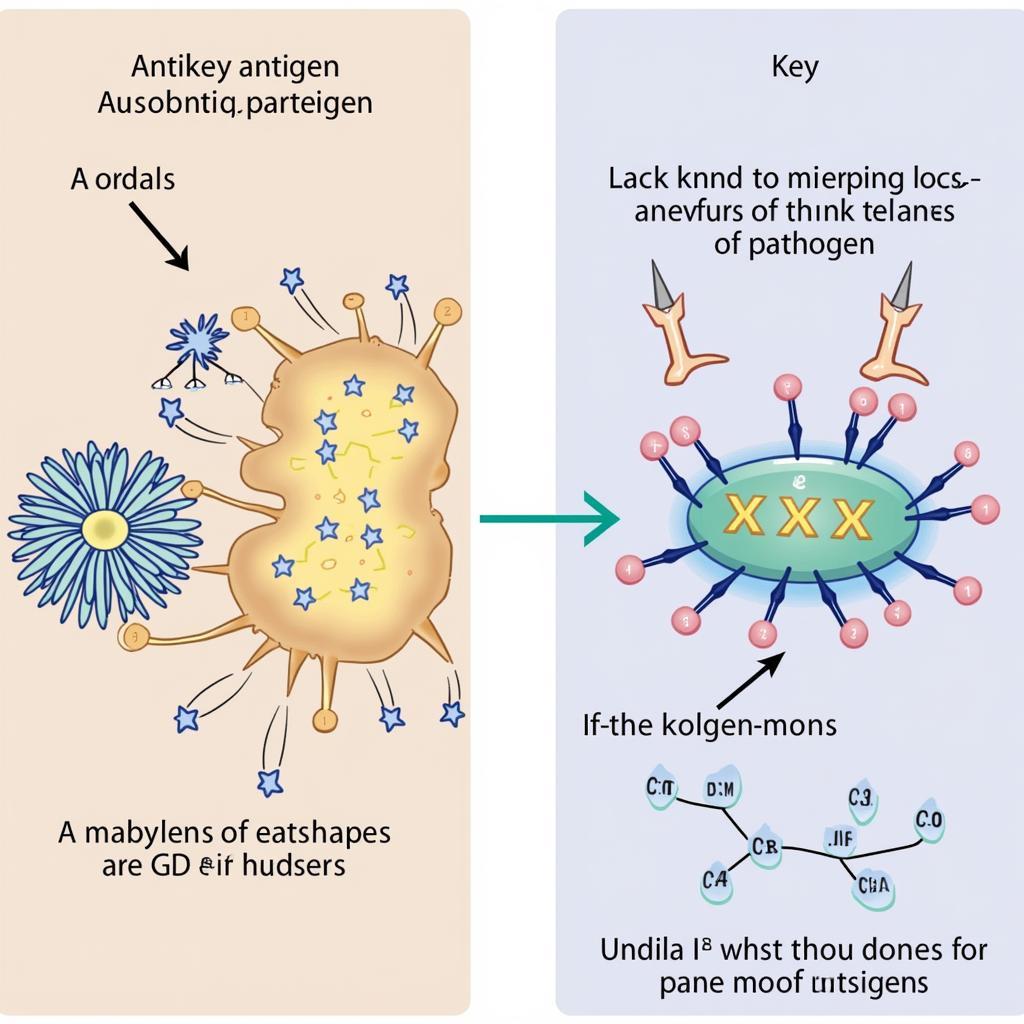 Kháng nguyên và kháng thể
Kháng nguyên và kháng thể
The Key Differences: Antigens vs. Pathogens
The crucial difference lies in their function: pathogens cause disease, while antigens trigger an immune response. Not all antigens are harmful; in fact, many are harmless substances from our environment, like pollen or dust. However, when our immune system overreacts to these harmless antigens, it can lead to allergies.
- Pathogens: Cause disease
- Antigens: Trigger immune response, not necessarily harmful
How the Immune System Responds to Antigens
Our immune system is a complex network of cells and proteins that work together to protect us from harmful invaders. When an antigen is detected, the immune system launches a targeted attack, producing antibodies that bind specifically to the antigen, marking it for destruction.
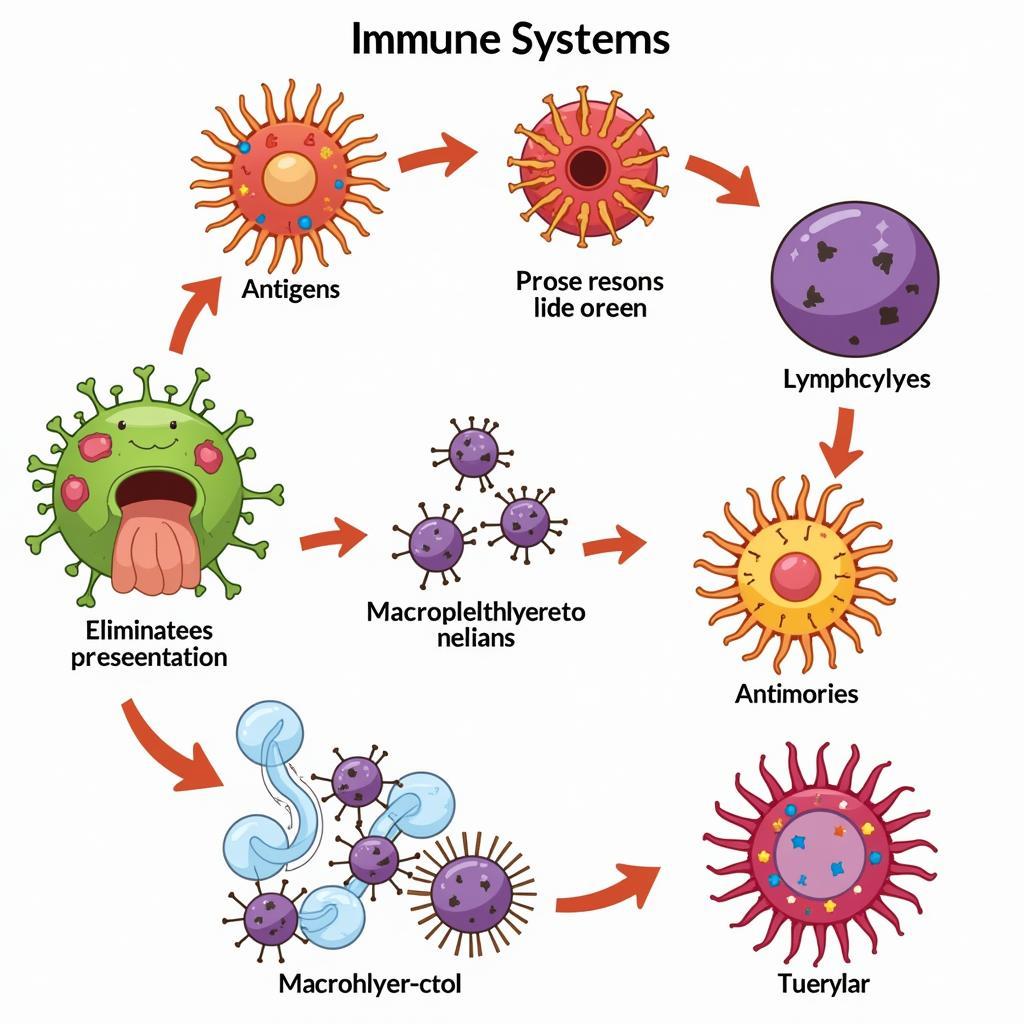 Phản ứng miễn dịch với kháng nguyên
Phản ứng miễn dịch với kháng nguyên
Example: The Flu Virus
The influenza virus (the flu) is a pathogen. On its surface, it has specific proteins that act as antigens. When we are infected with the flu, our immune system recognizes these antigens as foreign and mounts an immune response to eliminate the virus.
The Importance of Understanding Antigens and Pathogens
Understanding the difference between antigens and pathogens is crucial for comprehending how our immune system works and how diseases develop. This knowledge is also essential for developing effective vaccines and treatments. Vaccines work by introducing harmless versions of antigens to our immune system, teaching it to recognize and fight off future infections.
Expert Insight
Dr. Nguyễn Văn An, Immunologist: “The relationship between antigens and pathogens is fundamental to immunology. Understanding how the immune system recognizes and responds to antigens is key to developing new strategies for preventing and treating infectious diseases.”
Conclusion: Antigens vs. Pathogens – Two Sides of the Same Coin
In the battle against disease, understanding the difference between antigens and pathogens is paramount. Antigens act as the triggers, alerting our immune system to the presence of potentially harmful invaders like pathogens. While all pathogens have antigens, not all antigens belong to pathogens. By grasping this crucial distinction, we can better appreciate the intricate workings of our immune system and the development of effective strategies to combat disease.
FAQs
- Can antigens be part of our own bodies? (Yes, in autoimmune diseases, the immune system mistakenly attacks self-antigens.)
- Are all bacteria pathogens? (No, many bacteria are beneficial and even essential for our health.)
- How do vaccines work? (Vaccines introduce harmless antigens to train the immune system to fight future infections.)
- What is an autoimmune disease? (A condition where the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues.)
- Can allergies be considered an immune response to antigens? (Yes, allergies are an overreaction of the immune system to harmless antigens like pollen or dust.)
- What are some examples of common pathogens? (Examples include bacteria like E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus, viruses like influenza and HIV, and fungi like Candida.)
- How can I boost my immune system? (Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through proper nutrition, exercise, and stress management can support immune function.)
Mô tả các tình huống thường gặp câu hỏi.
Người dùng thường hay nhầm lẫn giữa kháng nguyên và mầm bệnh, dẫn đến việc tìm kiếm thông tin sai lệch. Bài viết này giúp làm rõ sự khác biệt giữa hai khái niệm này.
Gợi ý các câu hỏi khác, bài viết khác có trong web.
- Hệ miễn dịch hoạt động như thế nào?
- Các loại bệnh truyền nhiễm phổ biến.
- Vai trò của vắc xin trong phòng ngừa bệnh tật.