Depression brain scan vs. normal reveals key differences, offering insights into this complex mental health condition. This article delves into the science behind these scans, exploring what they show and how they aid in diagnosis and treatment.
How Brain Scans Illuminate Depression
Brain scans, such as fMRI and PET, provide a window into the intricate workings of the brain, allowing researchers and clinicians to observe activity patterns in individuals with depression compared to those without. These scans don’t offer a definitive diagnosis, but contribute significantly to understanding the neurological basis of depression.
Key Differences Observed in Brain Scans
Brain scans of individuals with depression often exhibit distinct patterns compared to normal brains. These differences typically center around activity levels in certain brain regions associated with mood regulation, motivation, and cognitive function. For instance, reduced activity in the prefrontal cortex, responsible for executive functions like planning and decision-making, is a common finding. Conversely, increased activity in the amygdala, the brain’s emotional center, particularly in response to negative stimuli, is also frequently observed. These variations in brain activity contribute to the emotional and cognitive symptoms characteristic of depression.
Furthermore, studies have shown alterations in the hippocampus, a region crucial for memory and learning, in individuals experiencing depression. This can manifest as a decrease in hippocampal volume, potentially contributing to cognitive difficulties often associated with the condition.
The Role of Neurotransmitters
Brain scans also indirectly reveal information about neurotransmitter function. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells. Imbalances in key neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine are strongly implicated in depression. While brain scans don’t directly measure neurotransmitter levels, they can show changes in brain activity in areas where these neurotransmitters are active, providing clues about their role in the disorder.
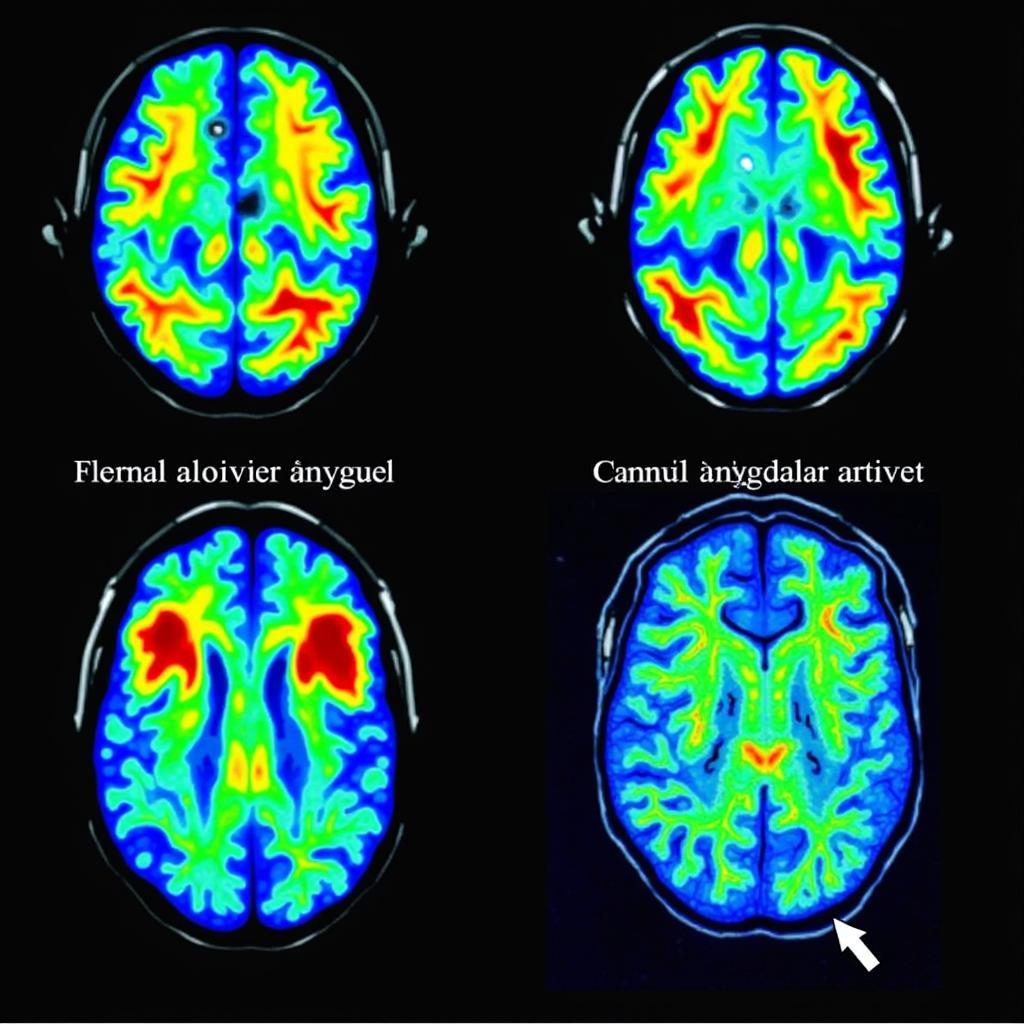 Amygdala Activity Changes in Depression
Amygdala Activity Changes in Depression
Using Brain Scans in Diagnosis and Treatment
Brain scans are not a standalone diagnostic tool for depression. A diagnosis relies on a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and psychological assessment. However, brain imaging can provide valuable supporting evidence, particularly in cases where the diagnosis is unclear or other medical conditions are suspected. Moreover, brain scans can be useful in monitoring treatment effectiveness. By tracking changes in brain activity over time, clinicians can assess whether a particular treatment is having the desired impact on the brain and adjust the treatment plan accordingly.
Limitations of Brain Scans in Depression
It’s important to acknowledge the limitations of brain scans in the context of depression. While they offer valuable insights, they are not perfect. Variations in brain activity can exist even among healthy individuals, and the changes observed in depression are not always consistent or specific. Furthermore, the cost and accessibility of brain scans can be a barrier for many individuals.
Conclusion
Depression brain scan vs. normal comparisons reveal critical differences in brain activity, shedding light on the neurobiological underpinnings of this pervasive mental health condition. While brain scans are not a definitive diagnostic tool, they contribute valuable information to aid in understanding, diagnosing, and managing depression. Further research continues to refine our understanding of these brain changes and their implications for treatment. If you are struggling with depression, seeking professional help is crucial.
FAQ
- Can a brain scan diagnose depression?
No, a brain scan cannot definitively diagnose depression. It is a supplementary tool used alongside other diagnostic methods. - What type of brain scan is used for depression?
fMRI and PET scans are commonly used to study brain activity in individuals with depression. - What do brain scans show in depressed individuals?
Brain scans may reveal differences in activity levels in certain brain regions associated with mood regulation and cognitive function. - Are brain scans necessary for depression treatment?
No, brain scans are not routinely required for depression treatment. - Are there any risks associated with brain scans?
While generally safe, certain types of brain scans may involve exposure to radiation or contrast agents. - How much does a brain scan cost?
The cost of a brain scan varies depending on the type of scan and location. - Can brain scans be used to monitor treatment effectiveness?
Yes, brain scans can track changes in brain activity over time, helping assess treatment response.
Possible related articles on our website:
- Understanding the Symptoms of Depression
- Treatment Options for Depression
- The Impact of Depression on Daily Life
For further assistance or information, please contact us at Phone Number: 02838172459, Email: [email protected] Or visit our address: 596 Đ. Hậu Giang, P.12, Quận 6, Hồ Chí Minh 70000, Vietnam. Our customer service team is available 24/7.