Biopsy and autopsy are both medical procedures involving tissue examination, but they serve distinct purposes and are performed under different circumstances. This article will delve into the critical differences between biopsy vs. autopsy, highlighting their specific applications and procedures.
What is a Biopsy?
A biopsy involves removing a small tissue sample from a living person for examination under a microscope. It’s a diagnostic procedure used to detect various conditions, from infections to cancer. There are different types of biopsies, including needle biopsies, incisional biopsies, and excisional biopsies, each tailored to specific situations. The goal of a biopsy is to identify the cause of an illness or abnormality and guide treatment decisions.
What is an Autopsy?
An autopsy, also known as a post-mortem examination, is a thorough examination of a deceased person’s body to determine the cause and manner of death. It involves a detailed examination of both external and internal organs. Autoversies are crucial for legal investigations, medical research, and understanding disease processes. They provide valuable insights into the circumstances surrounding death and can help prevent similar incidents in the future.
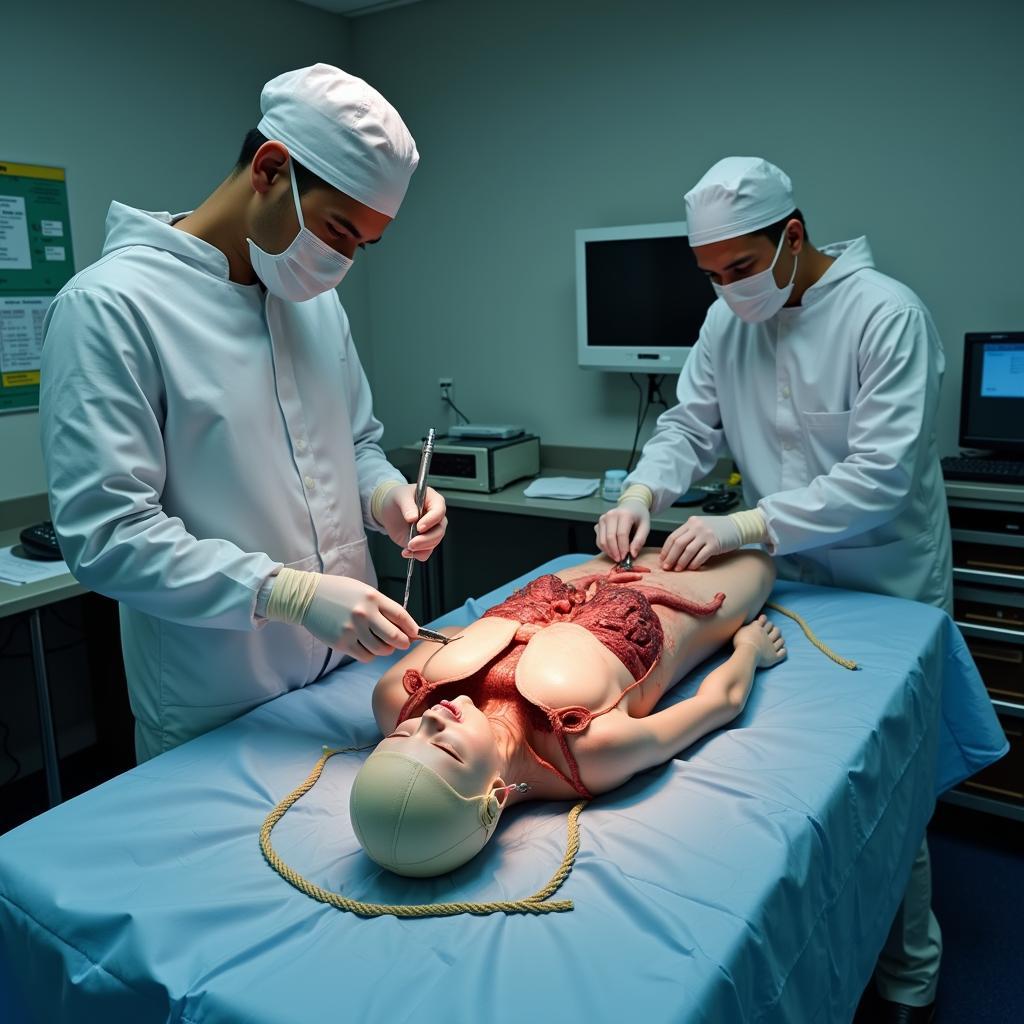 Autopsy examination
Autopsy examination
Biopsy vs. Autopsy: Key Differences
A key difference between a biopsy and an autopsy is the timing of the procedure: biopsies are performed on living individuals, while autopsies are conducted on deceased individuals. Another major distinction lies in their purpose. Biopsies primarily serve diagnostic purposes, aiming to identify diseases and guide treatment. Autopsies, on the other hand, focus on determining the cause and manner of death.
Procedure Differences
The procedures themselves also differ significantly. Biopsies are typically minimally invasive, often involving a small incision or needle insertion. Autopsies, by contrast, are more extensive, requiring a comprehensive examination of the entire body.
Who Performs the Procedure?
Biopsies are typically performed by surgeons, radiologists, or gastroenterologists, while autopsies are conducted by pathologists.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between biopsy vs. autopsy is crucial. Both procedures provide invaluable medical information, but they serve distinct purposes and are performed under different circumstances. A biopsy helps diagnose illnesses in living individuals, guiding treatment decisions. An autopsy helps determine the cause and manner of death, providing crucial information for legal and medical purposes.
FAQ
- Is a biopsy painful?
A biopsy can cause some discomfort, but local anesthesia is often used to minimize pain. - How long does an autopsy take?
An autopsy can take several hours to complete. - Are all deaths autopsied?
No, autopsies are not performed on all deaths. They are typically conducted in cases of sudden, unexpected, or suspicious deaths. - Who authorizes an autopsy?
Authorization for an autopsy may come from the next of kin, a medical examiner, or a coroner. - Can I refuse an autopsy?
In some cases, family members can refuse an autopsy, but there may be legal exceptions. - What are the risks of a biopsy?
The risks of a biopsy are generally low but can include bleeding, infection, and pain. - How accurate are autopsy results?
Autopsy results are generally considered highly accurate in determining the cause of death.
Kêu gọi hành động: Khi cần hỗ trợ hãy liên hệ Số Điện Thoại: 02838172459, Email: [email protected] Hoặc đến địa chỉ: 596 Đ. Hậu Giang, P.12, Quận 6, Hồ Chí Minh 70000, Việt Nam. Chúng tôi có đội ngũ chăm sóc khách hàng 24/7.