Epithelium vs. mucosa: These two terms are often confused, but they represent distinct biological structures. Understanding their differences is crucial for anyone studying human biology or related fields. This article will delve into the specifics of each, highlighting their unique functions and locations within the body.
What is Epithelium?
Epithelium is a type of tissue that covers the surfaces of the body, both internal and external. It acts as a protective barrier, shielding the underlying tissues from damage, pathogens, and dehydration. Think of it as the body’s “first line of defense.” Epithelial tissue also plays a role in secretion, absorption, and sensation.
Types of Epithelium
There are various types of epithelium, each specialized for a particular function:
- Simple squamous epithelium: Thin and flat, facilitating diffusion and filtration (e.g., lining of blood vessels).
- Stratified squamous epithelium: Multi-layered for protection in areas of high abrasion (e.g., skin).
- Cuboidal epithelium: Cube-shaped, involved in secretion and absorption (e.g., kidney tubules).
- Columnar epithelium: Tall and column-shaped, often with cilia or microvilli for increased surface area (e.g., lining of the digestive tract).
What is Mucosa?
Mucosa, also known as a mucous membrane, is a more complex structure that lines various cavities and canals in the body that open to the external environment, such as the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive tracts. It’s comprised of not only epithelium, but also connective tissue (lamina propria) and sometimes a thin layer of smooth muscle (muscularis mucosae). The mucosa secretes mucus, a viscous substance that lubricates and protects these delicate linings.
Functions of Mucosa
The mucosa performs several crucial functions depending on its location:
- Protection: The mucus secreted by the mucosa acts as a physical barrier, trapping pathogens and preventing them from entering the body.
- Lubrication: Mucus keeps the lining moist, facilitating the passage of substances (e.g., food in the digestive tract).
- Absorption: In the digestive tract, the mucosa absorbs nutrients from food.
- Secretion: The mucosa can secrete enzymes and other substances necessary for various bodily functions.
Epithelium vs. Mucosa: The Key Differences
So, what’s the main difference between epithelium and mucosa? Epithelium is a single type of tissue, while mucosa is a more complex structure comprising epithelium, connective tissue, and sometimes smooth muscle. Think of it this way: epithelium is a component of mucosa.
Comparing Epithelium and Mucosa
| Feature | Epithelium | Mucosa |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Epithelial cells | Epithelium, connective tissue, smooth muscle |
| Location | Covers all body surfaces (internal & external) | Lines cavities open to the exterior |
| Function | Protection, secretion, absorption, sensation | Protection, lubrication, absorption, secretion |
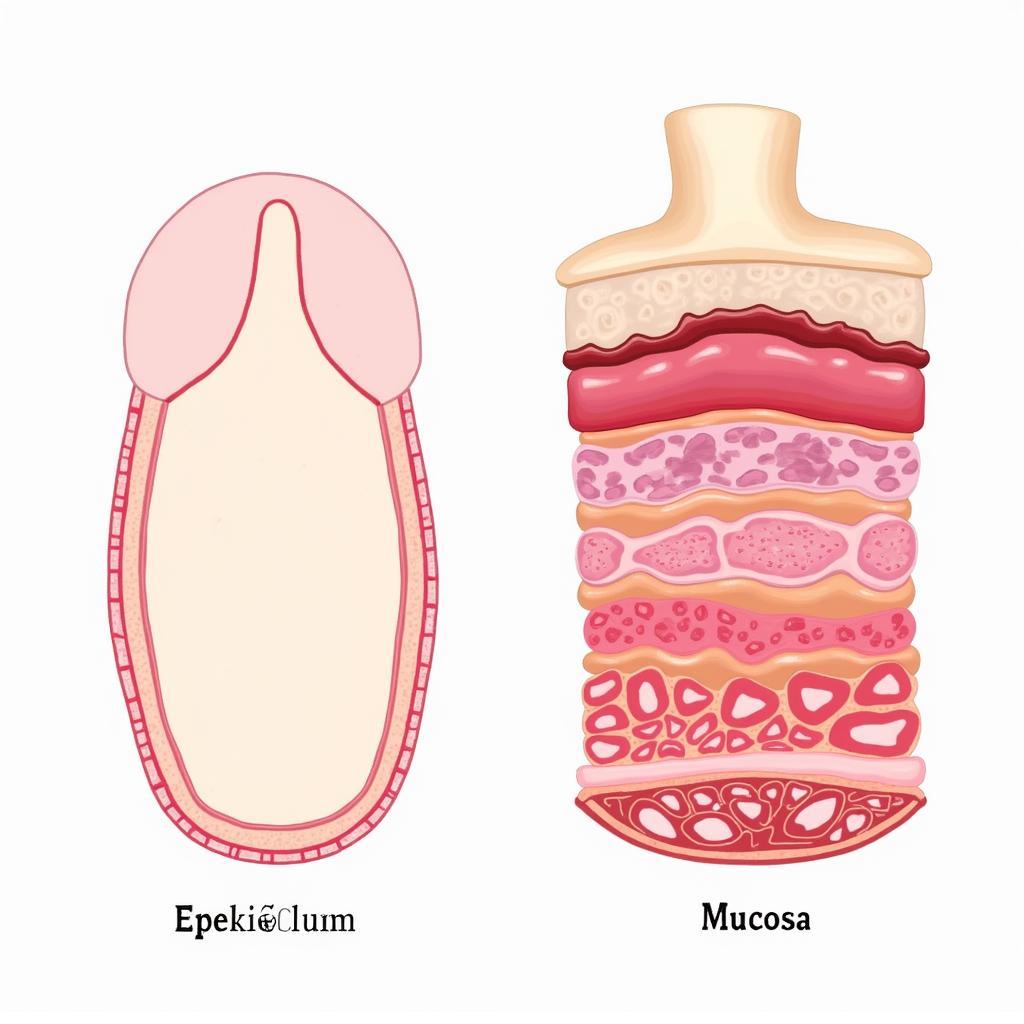 So sánh biểu mô và niêm mạc
So sánh biểu mô và niêm mạc
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Is all epithelium part of a mucosa? No, epithelium can exist independently of mucosa, such as the epidermis of the skin.
- What is the role of mucus? Mucus acts as a protective barrier, trapping pathogens and lubricating surfaces.
- What are examples of mucosa in the body? The lining of the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive tracts are all examples of mucosa.
- Why is it important to understand the difference between epithelium and mucosa? Understanding the distinct structures and functions of epithelium and mucosa is crucial for comprehending human biology and related fields.
- What can cause damage to the mucosa? Infections, inflammation, and certain medical conditions can damage the mucosa.
Conclusion
Epithelium and mucosa, while related, are distinct biological structures. Epithelium forms the protective covering of all body surfaces, while mucosa, a more complex structure containing epithelium, lines cavities open to the exterior. Understanding this difference is fundamental for anyone studying biological systems. For further support, contact us at Phone: 02838172459, Email: [email protected] Or visit us at: 596 Đ. Hậu Giang, P.12, Quận 6, Hồ Chí Minh 70000, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.