Electric and electronic devices are ubiquitous in modern life, from the smartphones in our pockets to the appliances in our homes. While the terms are often used interchangeably, there’s a crucial distinction between electric and electronic devices. This article will delve into the core differences, helping you understand the nuances of these two closely related concepts.
The primary difference between electric and electronic devices lies in how they utilize electricity. Electric devices primarily use electricity to generate power, heat, or light, while electronic devices manipulate electricity to process information or perform specific tasks. This fundamental difference impacts their design, functionality, and application. Let’s explore these aspects in more detail.
What is an Electric Device?
Electric devices are designed to convert electrical energy into other forms of energy, such as heat, light, or mechanical motion. They typically involve a simple circuit that allows electricity to flow through a conductive material, producing the desired effect. Common examples include electric heaters, light bulbs, and motors. These devices generally do not involve complex circuitry or information processing.
What is an Electronic Device?
Electronic devices, on the other hand, use electricity to control the flow of electrons in more complex ways. They involve electronic components like transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits to manipulate electrical signals, enabling them to perform tasks such as amplification, computation, and data storage. Examples of electronic devices include computers, smartphones, televisions, and radios. Their ability to process information sets them apart from electric devices.
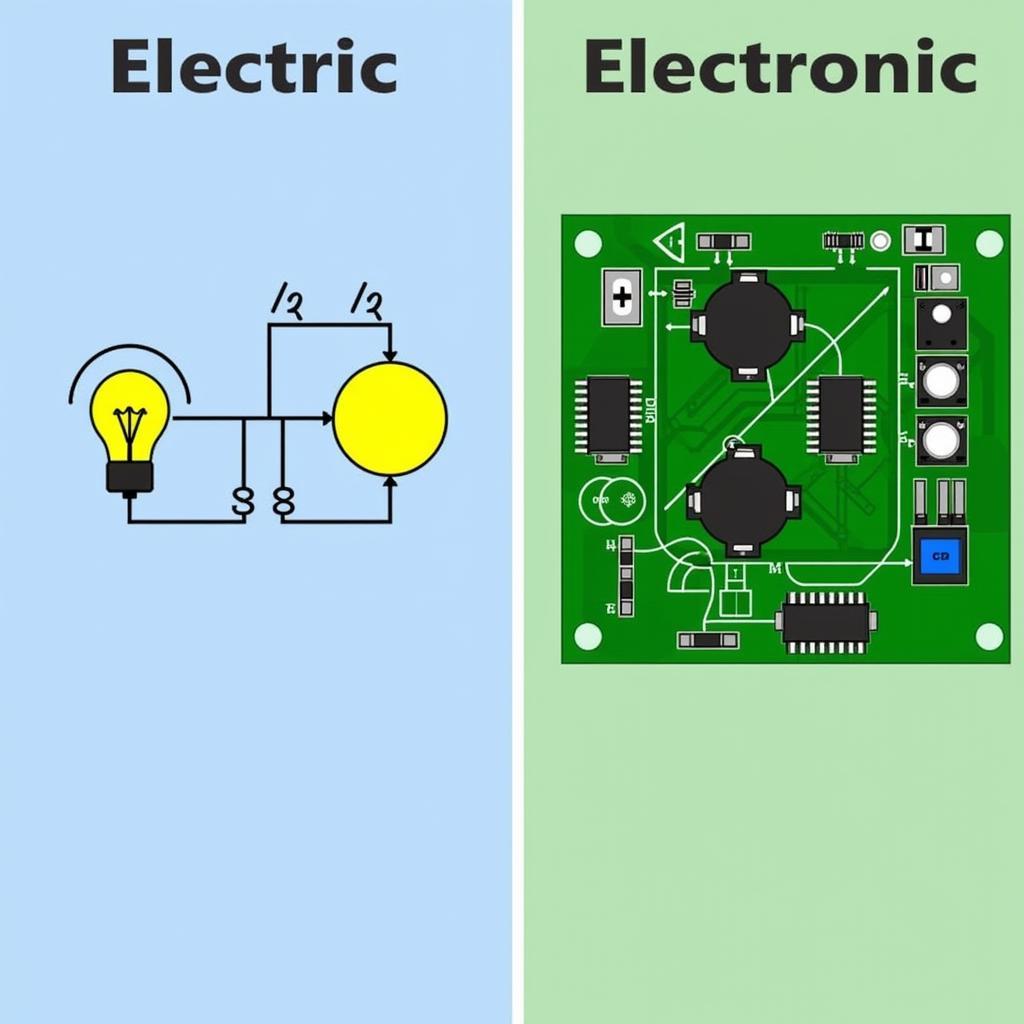 Sự khác biệt giữa thiết bị điện và điện tử
Sự khác biệt giữa thiết bị điện và điện tử
Key Differences: Electric vs. Electronic
Understanding the core differences between electric and electronic devices can be crucial in various contexts, from choosing the right appliance to troubleshooting technical issues. Here’s a breakdown of the key distinctions:
- Functionality: Electric devices primarily generate power, heat, or light. Electronic devices process information, control other devices, or perform specific tasks.
- Complexity: Electric devices have simpler circuitry. Electronic devices involve complex circuitry with integrated circuits and various components.
- Information Processing: Electric devices do not process information. Electronic devices manipulate electrical signals to process and store data.
- Control: Electric devices typically lack complex control mechanisms. Electronic devices often incorporate sophisticated control systems.
For instance, an electric oven uses electricity to generate heat for cooking, while a microwave oven, an electronic device, uses electricity to generate electromagnetic waves that cook food and also incorporates electronic controls for setting cooking times and power levels.
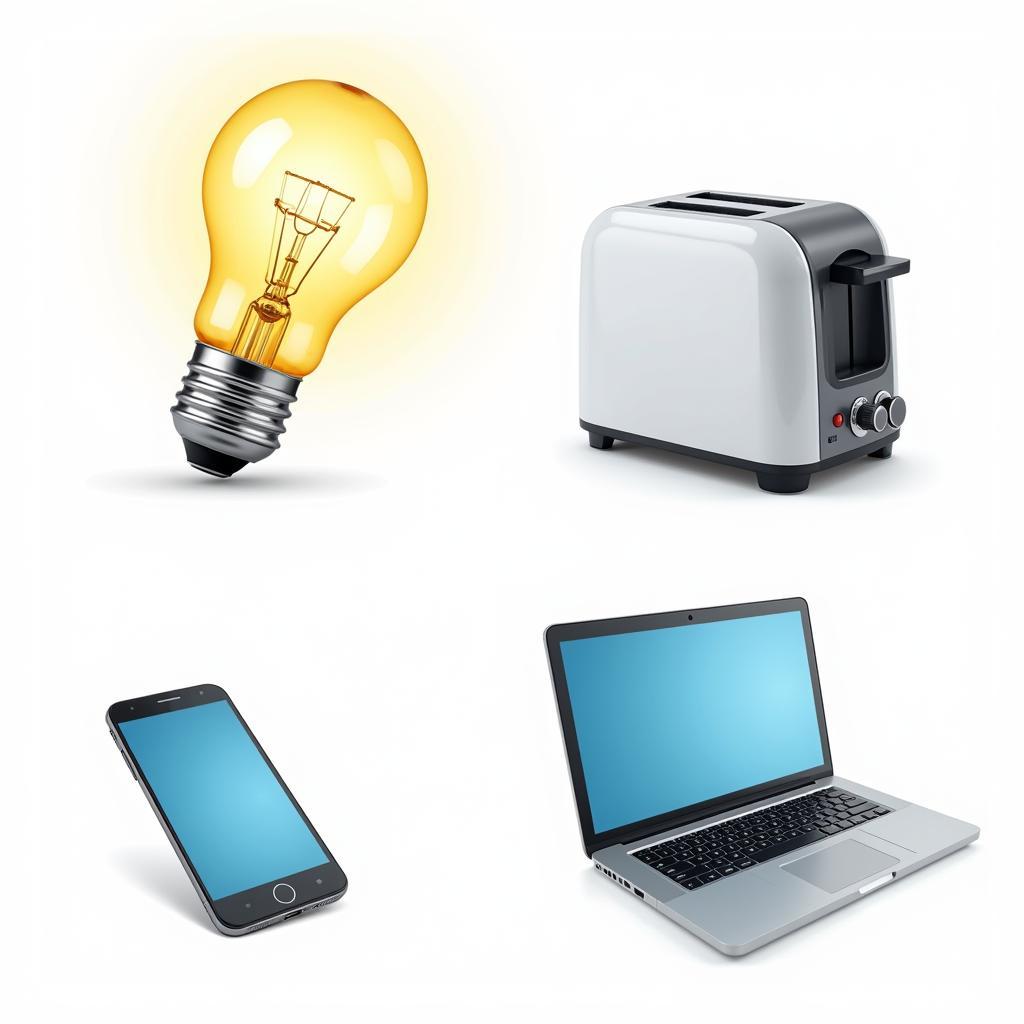 Ví dụ về thiết bị điện và điện tử
Ví dụ về thiết bị điện và điện tử
Electric vs Electrical: A Related Distinction
It’s also important to distinguish between “electric” and “electrical.” While they both relate to electricity, “electric” refers to something that produces or operates by electricity, while “electrical” describes something related to or concerned with electricity. For example, an electric car uses electricity for power, while an electrical engineer studies and designs systems that use electricity. You can find a more in-depth comparison of these two terms in our article on electric vs electrical.
Why is This Distinction Important?
Understanding the difference between electric and electronic is essential for several reasons:
- Troubleshooting: Knowing the type of device helps diagnose issues effectively. An electric device problem might involve a faulty connection, while an electronic device issue could be related to a malfunctioning component.
- Safety: Different safety precautions apply to electric and electronic devices. Handling high-voltage electric devices requires extreme caution, while electronic devices pose different risks, such as electrostatic discharge.
- Choosing the Right Device: Understanding the difference helps you select the appropriate device for your needs. If you need to heat a room, you’ll choose an electric heater, not an electronic device.
 Ứng dụng của thiết bị điện và điện tử
Ứng dụng của thiết bị điện và điện tử
Let’s consider the expertise of Dr. Nguyễn Văn A, a renowned electrical engineer: “The distinction between electric and electronic devices is fundamental to understanding the technological landscape. While both utilize electricity, their functions and complexities differ significantly, impacting their applications in diverse fields.”
Conclusion
While often confused, “electric” and “electronic” describe distinct types of devices. Electric devices primarily convert electrical energy into other forms, while electronic devices manipulate electricity to process information and perform complex tasks. Understanding this difference is crucial for choosing the right device, troubleshooting issues, and appreciating the diverse applications of electricity in our lives. Remember the key difference lies in their complexity and ability to process information. Keeping this in mind will help you navigate the world of electric and electronic devices more effectively.
FAQ
- What is the simplest example of an electric device? A simple light bulb.
- What is the simplest example of an electronic device? A simple transistor radio.
- Are all electronic devices also electric devices? Yes, because they all use electricity.
- Are all electric devices also electronic devices? No, because electric devices don’t necessarily involve electronic components or information processing.
- Why is a computer considered an electronic device? Because it uses electronic components to process and store information.
- Is a toaster electric or electronic? An electric toaster is primarily an electric device, while a toaster oven with electronic controls is both electric and electronic.
- Why is understanding this distinction important? It’s crucial for troubleshooting, safety, and selecting the right device for a specific purpose.
Have more questions about the differences between these types of technologies? Check out our article comparing bronze vs copper for a deeper understanding of material properties related to conductivity and electrical applications or 802.1 d vs 802.1 q for information on networking protocols that govern electronic communication.
Mô tả các tình huống thường gặp câu hỏi.
Một số tình huống thường gặp câu hỏi về Electric Vs Electronic bao gồm việc xác định loại thiết bị khi sửa chữa, lựa chọn thiết bị phù hợp cho nhu cầu sử dụng, hoặc khi tìm hiểu về công nghệ.
Gợi ý các câu hỏi khác, bài viết khác có trong web.
Ngoài ra, bạn có thể tìm hiểu thêm về các chủ đề liên quan như sự khác biệt giữa điện AC và DC, hoặc các loại linh kiện điện tử cơ bản.
Khi cần hỗ trợ hãy liên hệ Số Điện Thoại: 02838172459, Email: [email protected] Hoặc đến địa chỉ: 596 Đ. Hậu Giang, P.12, Quận 6, Hồ Chí Minh 70000, Việt Nam. Chúng tôi có đội ngũ chăm sóc khách hàng 24/7.