Linear analysis and nonlinear analysis are two fundamental approaches in engineering, mathematics, and physics for understanding and modeling systems. This article explores the core differences between these two methodologies, highlighting their applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
What is Linear Analysis?
Linear analysis deals with systems that exhibit a direct, proportional relationship between input and output. In simpler terms, if you double the input, you double the output. This proportionality allows for straightforward calculations and predictions. Linear systems adhere to the principle of superposition, meaning the combined effect of multiple inputs is equal to the sum of their individual effects.
Key characteristics of linear systems include:
- Proportionality: Output is directly proportional to input.
- Superposition: Combined effects of inputs are additive.
- Homogeneity: Scaling the input scales the output by the same factor.
Examples of linear systems include simple springs, resistors, and capacitors in basic electrical circuits. Linear analysis techniques, like Fourier transforms and Laplace transforms, are often used to analyze these systems.
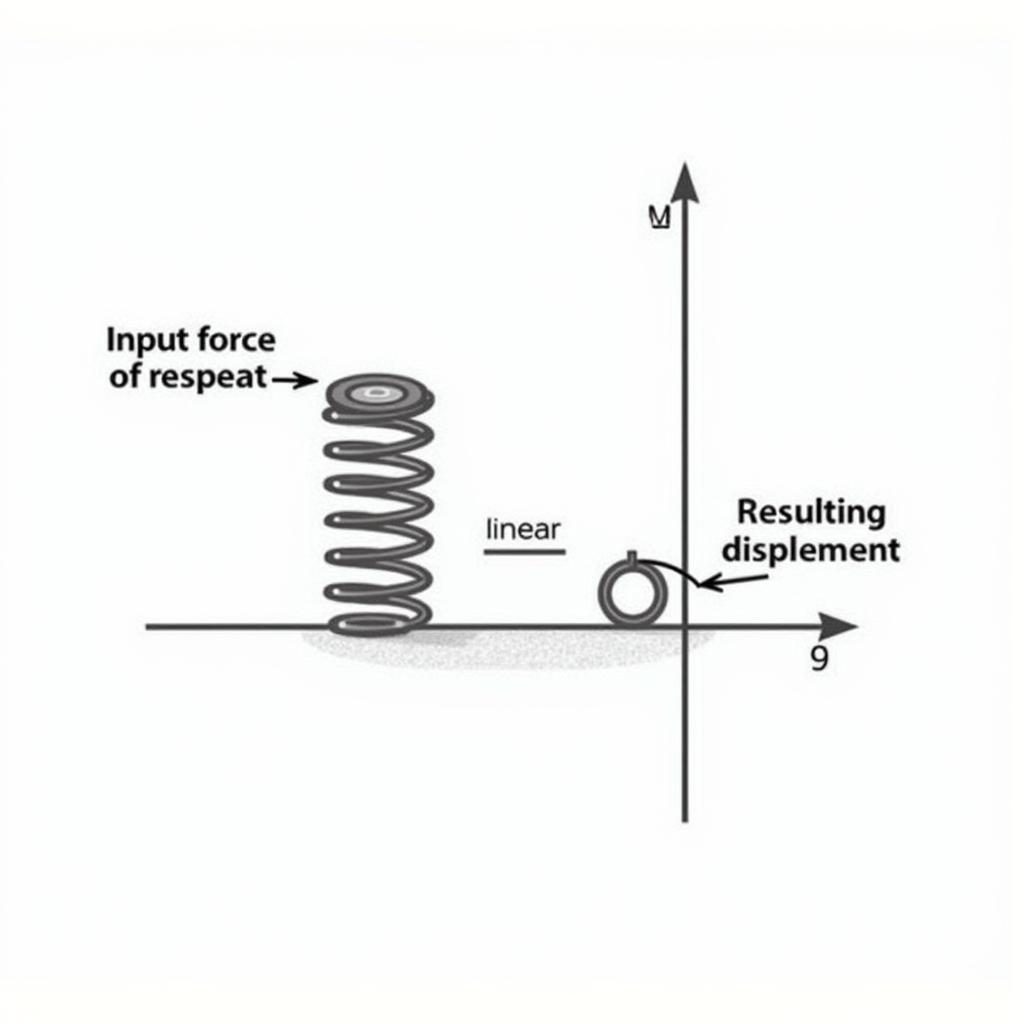 Phân tích tuyến tính trong hệ thống lò xo
Phân tích tuyến tính trong hệ thống lò xo
Diving into Nonlinear Analysis
Unlike linear analysis, nonlinear analysis deals with systems where the relationship between input and output is not proportional. A small change in input can lead to a disproportionate change in output, making these systems more complex to analyze and predict. Nonlinear systems do not follow the principle of superposition.
Characteristics of nonlinear systems:
- Non-proportionality: Output is not directly proportional to input.
- No superposition: Combined effects of inputs are not simply additive.
- Hysteresis: The system’s output depends on its past history.
- Chaos: Small changes in initial conditions can lead to drastically different outcomes.
Examples of nonlinear systems are abundant in the real world, including weather patterns, fluid dynamics, and the behavior of most biological systems.
 Mô phỏng dòng chảy chất lỏng phi tuyến
Mô phỏng dòng chảy chất lỏng phi tuyến
Linear Analysis vs Nonlinear Analysis: A Head-to-Head Comparison
A direct comparison between linear and nonlinear analysis can be summarized as follows:
| Feature | Linear Analysis | Nonlinear Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Input-Output | Proportional | Non-proportional |
| Complexity | Simpler | More complex |
| Superposition | Applies | Does not apply |
| Predictability | High | Lower |
| Real-world accuracy | Limited | Higher |
| Mathematical tools | Simpler | More advanced |
When to Use Which Analysis?
Choosing between linear and nonlinear analysis depends heavily on the specific system and the level of accuracy required. Linear analysis offers simplicity and is suitable for systems exhibiting approximate linearity within a specific range. However, for complex systems or when high accuracy is paramount, nonlinear analysis is necessary.
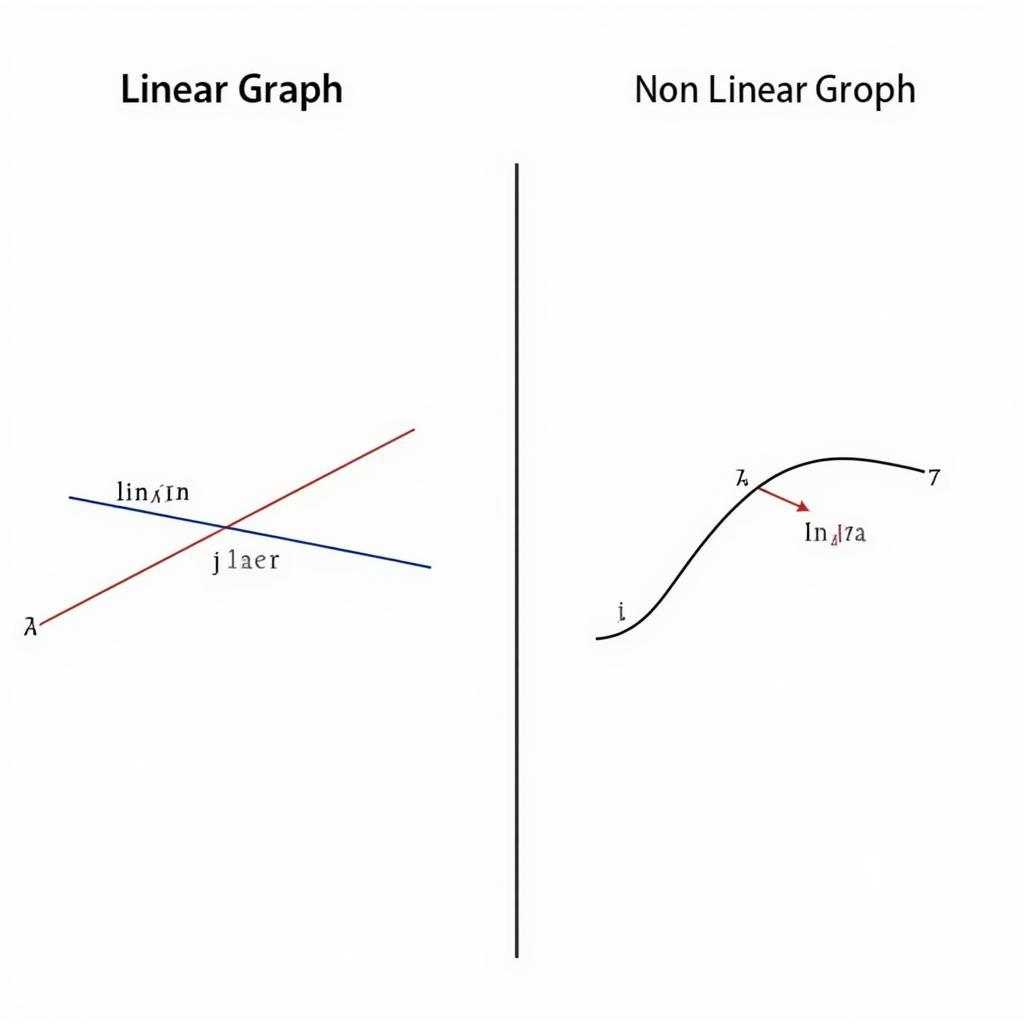 So sánh phân tích tuyến tính và phi tuyến
So sánh phân tích tuyến tính và phi tuyến
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
Understanding the key differences between linear analysis and nonlinear analysis is crucial for effectively modeling and analyzing various systems. While linear analysis provides simplified solutions for specific cases, nonlinear analysis offers a more realistic representation of many real-world phenomena. Choosing the right approach depends on the specific application, desired accuracy, and the complexity of the system under investigation. Remember that understanding these concepts allows for a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the world around us.
FAQ
- What is the principle of superposition?
Superposition is the principle that the net response caused by two or more stimuli is the sum of the responses which would have been caused by each stimulus individually. - Why is nonlinear analysis more complex?
Nonlinear analysis is more complex due to the non-proportional relationship between input and output and the absence of superposition. - What are some examples of nonlinear systems in everyday life?
Examples include weather patterns, the stock market, and the human body. - Can linear analysis be used to approximate nonlinear systems?
Yes, under certain limited conditions and within a specific range, linearization techniques can approximate nonlinear behavior. - What are some common mathematical tools used in nonlinear analysis?
Common tools include differential equations, numerical methods, and perturbation theory. - What is hysteresis in a nonlinear system?
Hysteresis refers to the dependence of the system’s output on its past history. - How does chaos affect nonlinear systems?
Chaos makes nonlinear systems highly sensitive to initial conditions, resulting in unpredictable long-term behavior.
Khi cần hỗ trợ hãy liên hệ Số Điện Thoại: 02838172459, Email: truyenthongbongda@gmail.com Hoặc đến địa chỉ: 596 Đ. Hậu Giang, P.12, Quận 6, Hồ Chí Minh 70000, Việt Nam. Chúng tôi có đội ngũ chăm sóc khách hàng 24/7.