The financial world can be confusing, especially when dealing with terms like “loanable funds market” and “money market.” This article will break down the key differences between the Loanable Funds Market Vs Money Market, helping you understand how these crucial components of the economy operate.
What is the Loanable Funds Market?
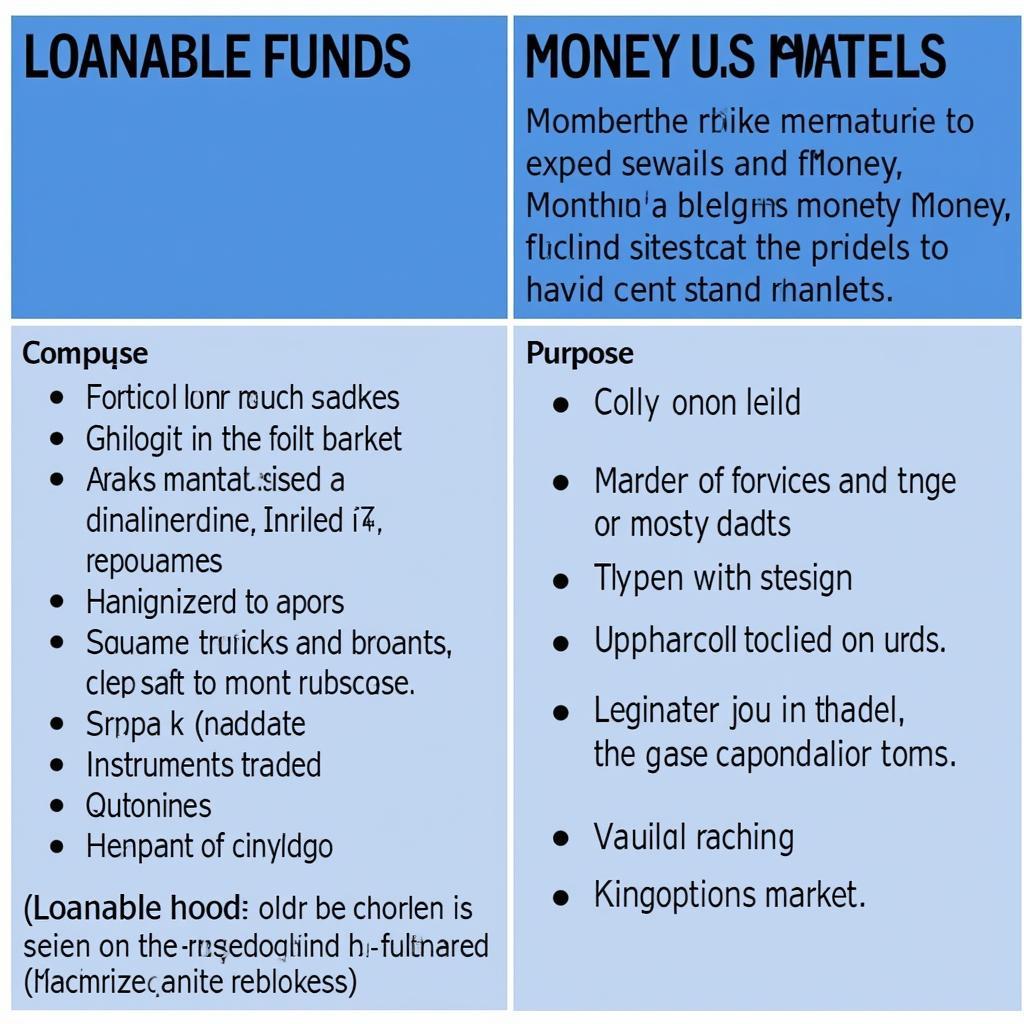
The loanable funds market focuses on the supply and demand of loanable funds over a long-term horizon, primarily for investments. The supply of loanable funds comes from savers, while the demand comes from borrowers, such as businesses seeking capital for expansion or individuals looking for mortgages. The interest rate acts as the price in this market, balancing supply and demand.
What is the Money Market?
The money market, conversely, deals with short-term, highly liquid debt instruments. It’s where businesses and governments raise short-term capital to manage cash flow and bridge financing gaps. Instruments traded in this market include treasury bills, commercial paper, and certificates of deposit. Like the loanable funds market, the interest rate plays a critical role in balancing supply and demand.
Key Differences Between Loanable Funds Market vs Money Market
Several factors distinguish the loanable funds market from the money market. These include:
- Time Horizon: Loanable funds are typically lent and borrowed for longer periods, often years or decades, while money market transactions are typically for periods of less than a year.
- Purpose: Loanable funds primarily finance long-term investments, while the money market addresses short-term liquidity needs.
- Instruments: The loanable funds market deals with instruments like mortgages and corporate bonds. The money market, on the other hand, trades short-term debt securities like treasury bills and commercial paper.
- Risk: Generally, loanable funds market investments carry a higher risk due to their longer maturity, while money market instruments are considered relatively low risk.
 So sánh Thị trường Vốn vay và Thị trường Tiền tệ
So sánh Thị trường Vốn vay và Thị trường Tiền tệ
How Interest Rates Affect Both Markets
Interest rates play a pivotal role in both markets. In the loanable funds market, a higher interest rate incentivizes saving, increasing the supply of loanable funds. Conversely, it discourages borrowing, reducing demand. In the money market, a higher interest rate attracts investors to short-term debt instruments, increasing demand and raising the price.
Why Understanding These Markets Matters
Understanding the loanable funds market vs money market is essential for grasping the dynamics of the financial system. It helps investors make informed decisions about where to allocate their capital, and it allows businesses to understand the options available for raising funds.
Loanable Funds Market vs Money Market: A Simple Analogy
Imagine you’re planning a vacation. Saving for the trip over several months represents the loanable funds market, a long-term investment. Borrowing a small amount to cover a last-minute expense represents the money market, a short-term solution.
What is the main difference between these markets?
The key difference is time horizon.
What is the function of the money market?
The money market helps manage short-term liquidity needs.
How does the interest rate affect the loanable funds market?
It balances the supply and demand of loanable funds.
Expert Insight: “Understanding the nuances of these markets empowers individuals and businesses to make sound financial decisions,” says Dr. Nguyễn Văn Tài, a renowned economist at the University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City.
Conclusion
The loanable funds market and money market are distinct yet interconnected components of the financial system. Understanding their differences, particularly in terms of time horizon and purpose, is crucial for navigating the complexities of finance and making informed decisions. Remember, long-term investments belong in the loanable funds market, while short-term liquidity needs are addressed by the money market.
Expert Insight: “Effective financial planning requires a deep understanding of how these markets operate,” adds Ms. Trần Thị Thu Hằng, a senior financial analyst at a leading investment firm in Hanoi. “Recognizing the differences between them is the first step towards making smart investment and borrowing choices.”
FAQ
- What is the primary function of the loanable funds market? (To facilitate long-term investments)
- What types of instruments are traded in the money market? (Short-term debt securities like treasury bills and commercial paper)
- What is the key factor differentiating the loanable funds market from the money market? (Time horizon)
- How do interest rates impact both markets? (They influence supply and demand)
- Why is it important to understand these markets? (To make informed financial decisions)
- Who are the main participants in the loanable funds market? (Savers and Borrowers)
- What is an example of a loanable funds market transaction? (Mortgage loan)
Khi cần hỗ trợ hãy liên hệ Số Điện Thoại: 02838172459, Email: [email protected] Hoặc đến địa chỉ: 596 Đ. Hậu Giang, P.12, Quận 6, Hồ Chí Minh 70000, Việt Nam. Chúng tôi có đội ngũ chăm sóc khách hàng 24/7.