Macropinocytosis and endocytosis are both cellular processes involved in taking in substances from the outside environment. While they share similarities, they also have distinct mechanisms and purposes. This article dives deep into macropinocytosis vs. endocytosis, exploring their differences and highlighting their importance in cellular function.
Understanding Endocytosis: The Basics
Endocytosis is a general term for the process by which cells internalize substances by engulfing them within a membrane-bound vesicle. Think of it as the cell’s way of “eating” and “drinking.” There are various types of endocytosis, including phagocytosis (“cell eating” of larger particles), pinocytosis (“cell drinking” of fluids and dissolved solutes), and receptor-mediated endocytosis (highly specific uptake of molecules bound to receptors). These processes are crucial for nutrient uptake, immune responses, and cell signaling.
Exploring Macropinocytosis: A Unique Form of Endocytosis
Macropinocytosis is a specialized form of endocytosis that involves the non-specific uptake of large amounts of extracellular fluid and its contents. Unlike other types of endocytosis, macropinocytosis doesn’t rely on receptors to bind to specific molecules. Instead, it uses membrane ruffles, extensions of the cell membrane, to enclose large volumes of fluid and form macropinosomes. These macropinosomes are larger than the vesicles formed during other endocytotic processes.
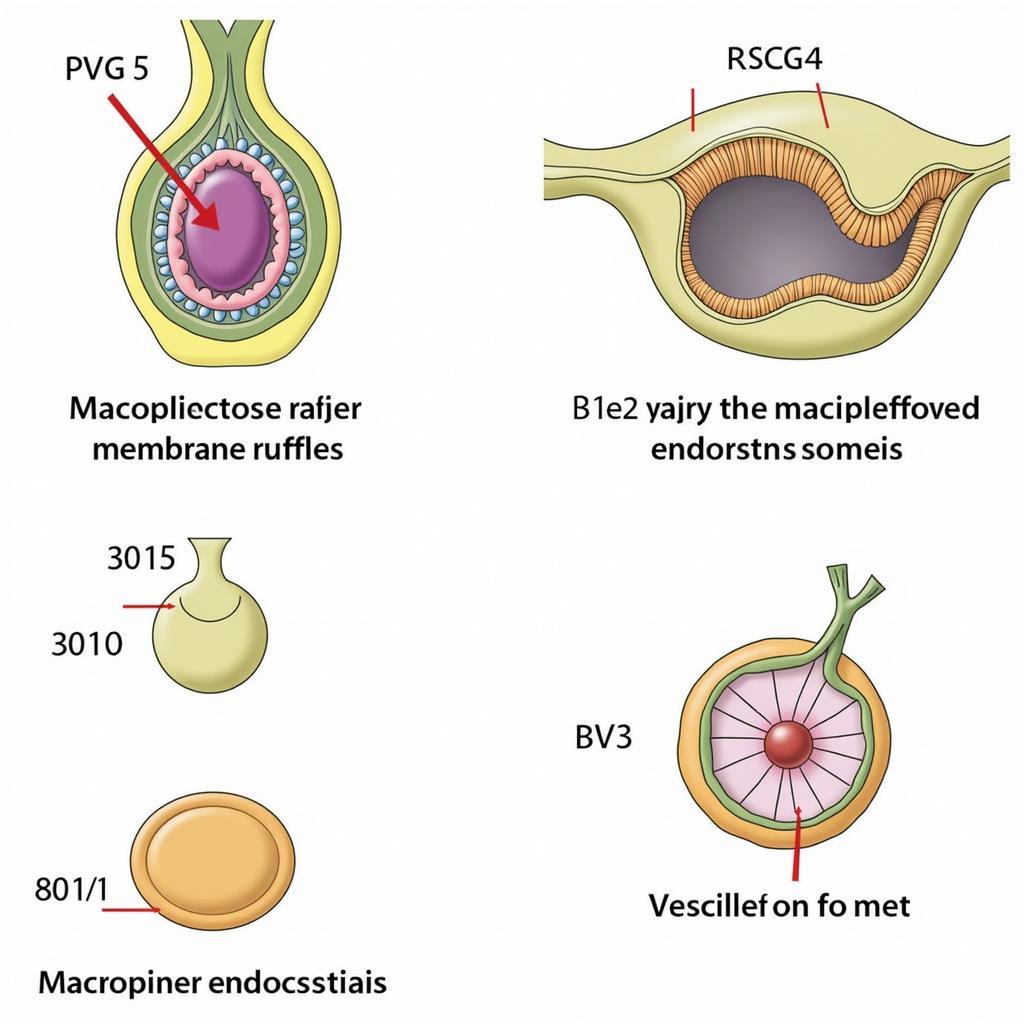 So sánh cơ chế Macropinocytosis và Endocytosis
So sánh cơ chế Macropinocytosis và Endocytosis
Macropinocytosis vs. Endocytosis: Key Differences
While both involve internalizing extracellular material, macropinocytosis and other forms of endocytosis differ in several ways:
- Specificity: Endocytosis can be highly specific, particularly receptor-mediated endocytosis, while macropinocytosis is non-specific and takes in whatever is present in the surrounding fluid.
- Size: Macropinosomes are significantly larger than the vesicles formed during other endocytotic processes.
- Mechanism: Macropinocytosis uses membrane ruffles, while other forms of endocytosis use different mechanisms, such as clathrin-coated pits or caveolae.
- Purpose: Endocytosis serves a variety of functions, including nutrient uptake and cell signaling. Macropinocytosis is primarily involved in bulk fluid uptake, antigen presentation, and cell migration.
What is the main difference between macropinocytosis and other endocytosis processes?
The main difference lies in the specificity of uptake. Macropinocytosis is non-specific, engulfing large amounts of extracellular fluid and its contents, while other forms of endocytosis, such as receptor-mediated endocytosis, are highly specific, targeting and internalizing particular molecules.
What is the role of macropinocytosis in immune response?
Macropinocytosis plays a key role in antigen presentation by capturing antigens from the extracellular environment and delivering them to lysosomes for processing. These processed antigens are then displayed on the cell surface for recognition by T cells, initiating an immune response.
How does macropinocytosis contribute to cell migration?
Macropinocytosis contributes to cell migration by regulating membrane trafficking and cell surface area. By internalizing large portions of the plasma membrane through macropinosome formation, cells can dynamically remodel their surface and facilitate movement.
Why is understanding the difference between macropinocytosis and endocytosis important?
Understanding the distinction between macropinocytosis and endocytosis is crucial for comprehending various cellular processes, including nutrient uptake, immune responses, and cell migration. This knowledge is essential for developing new therapies for diseases like cancer and infections.
 Ứng dụng Macropinocytosis trong điều trị ung thư
Ứng dụng Macropinocytosis trong điều trị ung thư
Conclusion
Macropinocytosis and endocytosis are vital cellular processes with distinct characteristics. While both involve internalization of extracellular material, they differ in their mechanisms, specificity, and roles within the cell. Understanding these differences is crucial for comprehending fundamental cellular functions and developing targeted therapies for various diseases. Further research into Macropinocytosis Vs Endocytosis promises to unveil new insights into cellular biology and open new avenues for therapeutic interventions.
FAQ
- What is the simplest way to distinguish between macropinocytosis and other forms of endocytosis? Macropinocytosis is non-specific and involves large fluid uptake, while other forms of endocytosis can be highly specific.
- What are some examples of substances taken up by macropinocytosis? Extracellular fluid, antigens, dissolved nutrients, and even some viruses can be taken up by macropinocytosis.
- How does the size of a macropinosome compare to other endocytic vesicles? Macropinosomes are generally much larger.
- Is macropinocytosis always beneficial for cells? No, some pathogens can exploit macropinocytosis to enter cells.
- What are the implications of understanding macropinocytosis for cancer treatment? Targeting macropinocytosis could offer new ways to deliver drugs into cancer cells or inhibit their growth.
- How does pinocytosis differ from macropinocytosis? Pinocytosis involves the uptake of smaller amounts of fluid and dissolved solutes, while macropinocytosis takes in larger volumes.
- Can macropinocytosis be targeted for drug delivery? Yes, research is exploring how to exploit macropinocytosis for delivering drugs into specific cell types.
Mô tả các tình huống thường gặp câu hỏi
Người dùng thường thắc mắc về sự khác biệt giữa macropinocytosis và endocytosis, vai trò của chúng trong hệ miễn dịch và quá trình di cư của tế bào, cũng như ứng dụng của macropinocytosis trong điều trị ung thư.
Gợi ý các câu hỏi khác, bài viết khác có trong web.
- Các loại endocytosis khác là gì?
- Cơ chế chi tiết của receptor-mediated endocytosis là gì?
- Sự liên quan giữa macropinocytosis và bệnh tật là gì?