Parathyroid hyperplasia and adenoma are two common causes of primary hyperparathyroidism, a condition characterized by excessive parathyroid hormone (PTH) production. Distinguishing between hyperplasia and adenoma is crucial for effective treatment. Radiology, especially imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT, and MRI, plays a vital role in this differentiation. This article explores the radiological differences between parathyroid hyperplasia and adenoma, providing valuable insights for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Understanding Parathyroid Hyperplasia and Adenoma
Parathyroid hyperplasia involves enlargement of all four parathyroid glands. While each gland may not be equally enlarged, the overall increase in parathyroid tissue leads to overproduction of PTH. In contrast, a parathyroid adenoma is a benign tumor affecting a single parathyroid gland. This single, enlarged gland becomes the primary source of excess PTH. Differentiating between these two conditions requires careful radiological examination.
The Role of Radiology in Diagnosis
Radiology offers several imaging modalities to evaluate parathyroid glands. High-resolution ultrasound is often the initial imaging technique, offering a non-invasive way to visualize the neck and locate enlarged parathyroid glands. CT and MRI provide more detailed images, especially for ectopic glands (parathyroid glands located outside their usual position). These imaging techniques help identify the number and location of enlarged glands, size differences, and other characteristics that differentiate hyperplasia from adenoma.
Ultrasound Imaging: First Line of Defense
Ultrasound is typically the first imaging modality used to evaluate suspected parathyroid disorders. It uses sound waves to create images of the parathyroid glands. In cases of adenoma, ultrasound usually reveals a single, well-defined hypoechoic (darker) nodule. Hyperplasia, on the other hand, might show multiple enlarged glands, though not always equally enlarged.
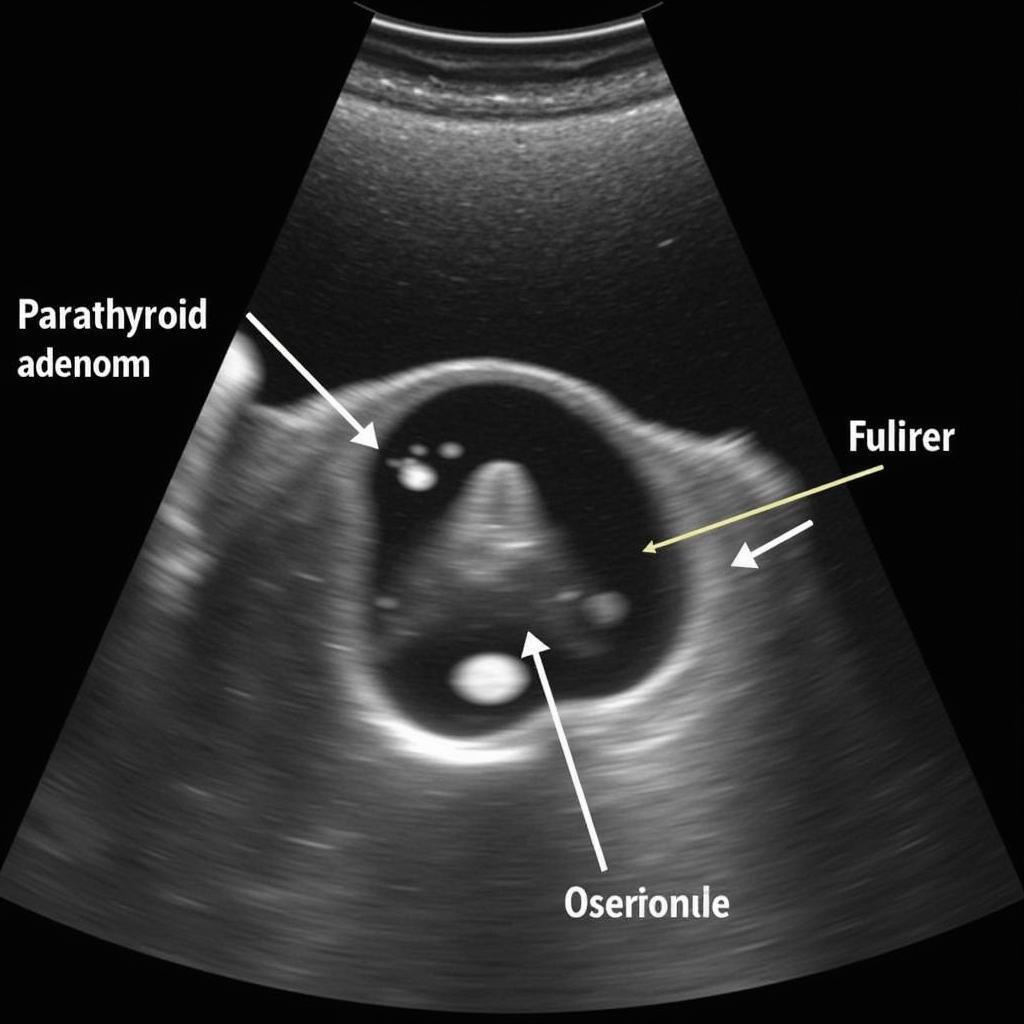 Siêu âm tuyến cận giáp: Phân biệt U nang tuyến cận giáp
Siêu âm tuyến cận giáp: Phân biệt U nang tuyến cận giáp
CT and MRI: Detailed Visualization
When ultrasound is inconclusive or when surgery is being planned, CT and MRI offer higher resolution images. CT scans provide excellent anatomical detail, particularly helpful in identifying ectopic parathyroid adenomas. MRI offers superior soft tissue contrast, which can help differentiate between adenoma and surrounding tissues. Both CT and MRI can contribute to accurate diagnosis and surgical planning.
Key Radiological Features for Differentiation
While overlapping features exist, some radiological characteristics can help distinguish between hyperplasia and adenoma. Adenomas are typically solitary, oval or round, and exhibit a distinct border. Hyperplasia often presents as multiple enlarged glands, but they might not be uniformly enlarged. The size discrepancy between glands is often less pronounced in hyperplasia than in adenoma cases. However, relying solely on size can be misleading, necessitating careful evaluation of all radiological features.
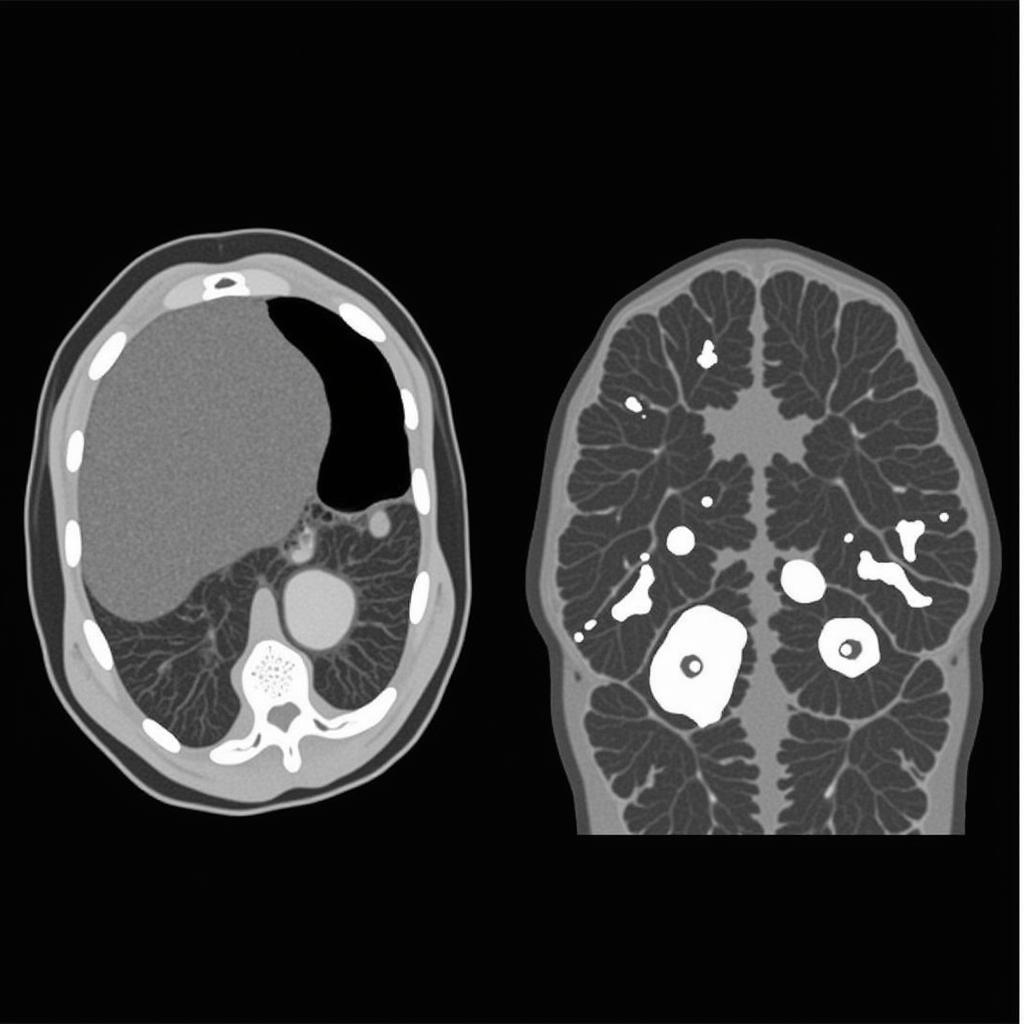 CT scan tuyến cận giáp: So sánh giữa U nang và Tăng sản
CT scan tuyến cận giáp: So sánh giữa U nang và Tăng sản
“In challenging cases, combining imaging modalities and correlating them with clinical and biochemical findings is essential for accurate diagnosis,” says Dr. Nguyen Van A, MD, a leading endocrinologist at Bach Mai Hospital.
Nuclear Medicine Scans: Functional Assessment
Nuclear medicine scans, such as sestamibi scans, are functional imaging techniques that assess parathyroid activity. These scans can be particularly useful in locating ectopic glands and confirming the diagnosis of adenoma, as they highlight areas of increased parathyroid activity. However, they are less helpful in differentiating hyperplasia from adenoma as both conditions can show increased uptake.
Conclusion
Differentiating between parathyroid hyperplasia and adenoma, crucial for effective treatment, heavily relies on radiology. Utilizing imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT, and MRI, alongside clinical and biochemical findings, enables precise diagnosis and informs appropriate management strategies. While challenges remain in certain cases, radiological advancements continue to improve our ability to differentiate these conditions, offering better outcomes for patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. Understanding the radiological features of both conditions, as discussed in this article, is essential for healthcare professionals involved in the diagnosis and treatment of parathyroid disorders.
 So sánh hình ảnh tăng sản và u nang tuyến cận giáp
So sánh hình ảnh tăng sản và u nang tuyến cận giáp
“Early diagnosis and appropriate intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes in hyperparathyroidism. Radiology plays a vital role in this process,” adds Dr. Tran Thi B, Head of Radiology at Cho Ray Hospital.
FAQ
- What is the most common imaging test for parathyroid disorders? Ultrasound is usually the initial imaging test.
- Can CT scans detect ectopic parathyroid glands? Yes, CT scans are particularly useful in identifying ectopic parathyroid adenomas.
- Are MRI scans always necessary? Not always. MRI is often used when other imaging studies are inconclusive or when surgery is planned.
- What is the role of nuclear medicine scans in parathyroid imaging? Nuclear medicine scans can help locate overactive parathyroid glands, especially ectopic glands.
- What is the difference in treatment between hyperplasia and adenoma? The treatment approach differs; adenoma usually requires surgical removal of the affected gland, while hyperplasia might involve removing several glands or a portion of each gland.
- Can radiology alone definitively diagnose parathyroid hyperplasia or adenoma? Not always. Correlation with clinical and biochemical findings is crucial.
- How accurate are these imaging tests in differentiating hyperplasia from adenoma? While these tests provide valuable information, there can be overlapping features, making definitive diagnosis challenging in some cases.
Potential Related Questions
- What are the symptoms of hyperparathyroidism?
- What are the long-term complications of untreated hyperparathyroidism?
- What are the different surgical approaches for parathyroid adenoma removal?
- How is parathyroid hyperplasia managed medically?
Khi cần hỗ trợ hãy liên hệ Số Điện Thoại: 02838172459, Email: [email protected] Hoặc đến địa chỉ: 596 Đ. Hậu Giang, P.12, Quận 6, Hồ Chí Minh 70000, Việt Nam. Chúng tôi có đội ngũ chăm sóc khách hàng 24/7.